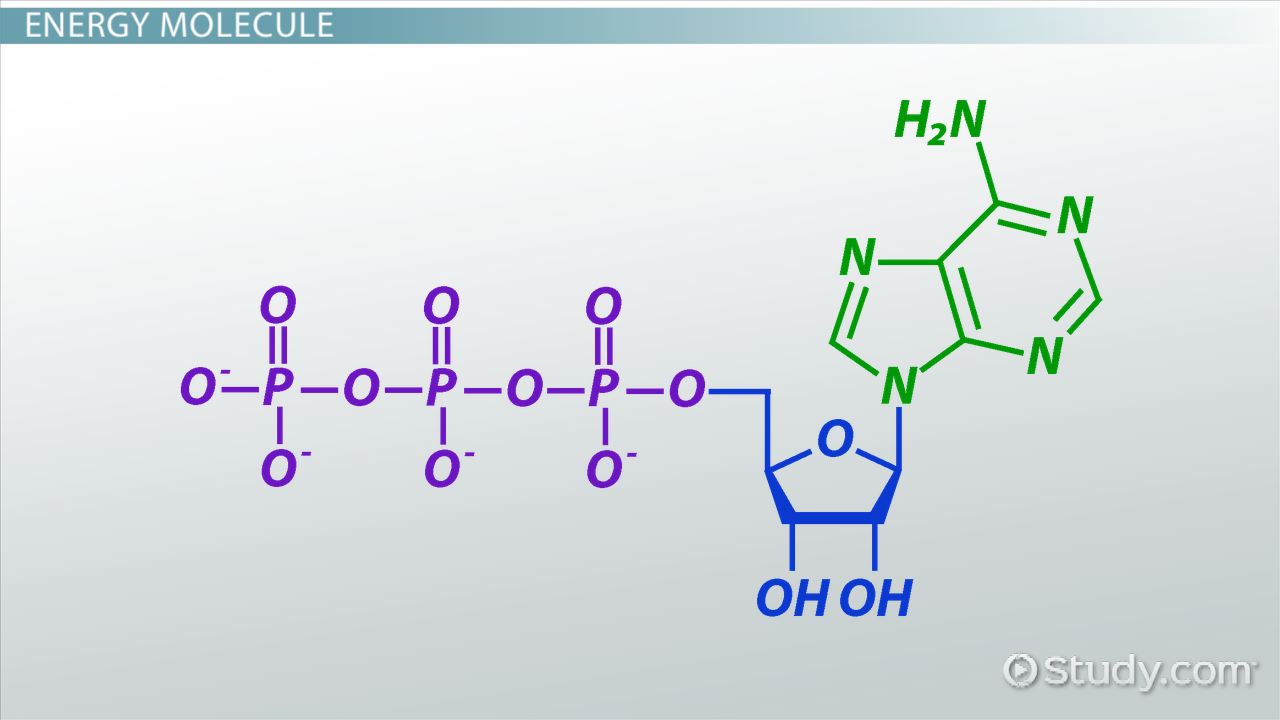
What Does Atp Stand For In Biology . Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and. atp is the energy currency for cellular processes. Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for cellular work. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. Learn how atp is synthesized, used, and. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. atp is adenosine triphosphate, the main form of energy currency in metabolism and cells. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be.
from study.com
atp is the energy currency for cellular processes. atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for cellular work. Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be. Learn how atp is synthesized, used, and. atp is adenosine triphosphate, the main form of energy currency in metabolism and cells. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells.
ATP Meaning, Structure & Formula Video & Lesson Transcript
What Does Atp Stand For In Biology Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for cellular work. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. atp is the energy currency for cellular processes. atp is adenosine triphosphate, the main form of energy currency in metabolism and cells. It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. Learn how atp is synthesized, used, and. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and.
From study.com
What is Adenosine Triphosphate? Definition, Function & Structure What Does Atp Stand For In Biology atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for cellular work. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and. Learn how atp is synthesized,. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From study.com
ATP Meaning, Structure & Formula Video & Lesson Transcript What Does Atp Stand For In Biology It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be. atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for cellular work. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. Learn how. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.biologyonline.com
ATP & ADP Biological Energy Biology Online Tutorial What Does Atp Stand For In Biology Learn how atp is synthesized, used, and. atp is adenosine triphosphate, the main form of energy currency in metabolism and cells. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.biologiedukasi.com
Jumlah ATP pada Respirasi Aerob Biologi Edukasi Belajar Sains Biologi What Does Atp Stand For In Biology atp is adenosine triphosphate, the main form of energy currency in metabolism and cells. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and. atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.sciencefacts.net
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Definition, Structure, & Diagram What Does Atp Stand For In Biology Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and. atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for cellular work. atp is the energy currency for cellular processes. Learn how atp is synthesized, used, and. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.brainkart.com
Structure of ATP What Does Atp Stand For In Biology atp is the energy currency for cellular processes. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. atp is adenosine triphosphate, the main form of energy currency in metabolism and cells. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT ATP PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1935407 What Does Atp Stand For In Biology Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. Learn how atp is synthesized, used, and. It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From masterofhealthyliving.com
What does ATP mean? Master of Healthy Living What Does Atp Stand For In Biology atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and.. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.youtube.com
ATP in Photosynthesis YouTube What Does Atp Stand For In Biology atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for cellular work. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be. Learn how atp is synthesized, used, and. atp. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From animalia-life.club
Atp Structure Labeled What Does Atp Stand For In Biology It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for cellular work. atp is adenosine triphosphate, the main form of energy currency in metabolism and. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.youtube.com
What is ATP & Where Does ATP Come From? YouTube What Does Atp Stand For In Biology Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. Learn how atp is synthesized, used, and. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.sliderbase.com
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Presentation Biology What Does Atp Stand For In Biology Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. atp is the energy currency for cellular processes. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. atp is a nucleotide. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.slideshare.net
ATP What Does Atp Stand For In Biology atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for cellular work. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be.. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.britannica.com
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts What Does Atp Stand For In Biology atp is adenosine triphosphate, the main form of energy currency in metabolism and cells. It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be. Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis and synthesis, and. atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.sliderbase.com
Bioenergetics Presentation Biology What Does Atp Stand For In Biology atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release free energy for cellular work. atp is the energy currency for cellular processes. Learn how atp is synthesized, hydrolyzed,. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. Learn how atp is synthesized, used, and. Learn about its molecular structure, hydrolysis. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From www.biologyonline.com
Adenosine triphosphate Definition and Examples Biology Online What Does Atp Stand For In Biology It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be. atp is adenosine triphosphate, the main form of energy currency in metabolism and cells. atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. atp. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From sciencenotes.org
What Is ATP in Biology? Adenosine Triphosphate Facts What Does Atp Stand For In Biology atp is a nucleotide that stores and transfers energy in cells. Learn how atp is synthesized, used, and. It is formed by adding phosphate groups to adenosine and can be. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. atp is the primary energy currency of cells that can be hydrolyzed to release. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.
From chemistrytalk.org
ChemTalk What is ATP in Biology? What Does Atp Stand For In Biology atp is adenosine triphosphate, the main form of energy currency in metabolism and cells. atp is the energy currency for cellular processes. atp is an organic molecule that supplies energy for all cellular activities in plants, animals, and lower organisms. atp is a nucleotide that captures and releases chemical energy for cellular processes. Learn how atp. What Does Atp Stand For In Biology.